Cm To Lbs Calculator – Convert Cubic Centimeters to Pounds
To convert centimeters to pounds, multiply the centimeter value by 0.393701, divide by 2.54, and then multiply by 0.453592.
To convert centimeters to pounds, multiply the centimeter value by 0.393701, divide by 2.54, and then multiply by 0.453592.
The Cm to Lbs Calculator provides an efficient way to convert measurements from centimeters to pounds. In general, it is used for height and weight conversions. This tool is useful in fields like fitness, health, and even engineering. Here, the act of converting between metric and imperial systems is often required.
By using this calculator, you can at once find the equivalent weight or height in pounds based on a given measurement in centimeters.
lbs = (cm ∗ 0.393701 / 2.54) ∗ 0.453592
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| lbs | Result in pounds |
| cm | Measurement in centimeters |
Example 1:
| Step | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Centimeter Value (cm) | 160 cm |
| Pounds Calculation | |
| Result | 140.8 lbs |
Answer: For a height or measurement of 160 cm, the equivalent is 140.8 lbs.
Example 2:
| Step | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Centimeter Value (cm) | 180 cm |
| Pounds Calculation | |
| Result | 158.7 lbs |
Answer: For a height or measurement of 180 cm, the equivalent is 158.7 lbs.
The Cm to Lbs Calculator is a powerful tool. This tool is utilized for converting height measurements in centimeters to an approximate weight in pounds. This metric is usually used in various health, fitness, and medical contexts.
While centimeters typically measure length, this calculator approximates weight conversion by factoring in an estimated average range based on the user’s height.
Using this calculator is simple: enter your height in centimeters, and it will estimate the equivalent weight range in pounds. This estimation provides a general idea of weight expectations but should be used with additional body measurements for a precise health assessment.
Last but not least, the Cm to Lbs Calculator offers a quick way to gauge weight from height measurements, bridging metric and imperial units for easier understanding in health and fitness contexts.
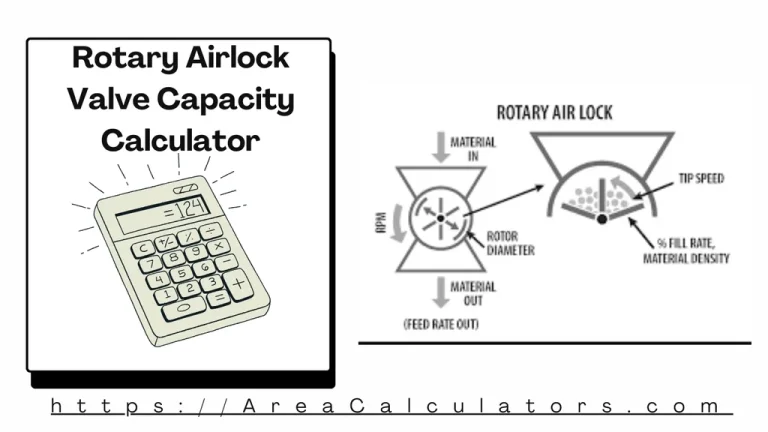
To find the capacity of a rotary airlock valve, divide the rotor displacement by material density, adjust for efficiency, and multiply by the rotor speed. The Rotary Airlock Valve Capacity Calculator is an indispensable tool for accurately determining the flow rate of materials in bulk handling systems. It considers critical variables such as rotor displacement,…
9 / 100 SEO Score To calculate the cost of smoking, divide the average number of cigarettes smoked per day by the number of cigarettes in a pack. Multiply that result by the cost per pack, then by 365 days in a year, and finally, multiply by the total number of years the person has…
To calculate the error bound using Simpson’s Rule, evaluate the maximum value of the fourth derivative of the function and apply it to the error formula for precise estimation. The Error Bound Calculator (Simpson’s Rule) helps estimate the error in numerical integration using Simpson’s Rule. It is an essential tool in numerical methods, providing accuracy…

10 / 100 SEO Score To calculate the calories burned from arm circles, multiply the MET value (2.8) by your body weight in kilograms and the duration of the activity in hours. This provides an estimate of how many calories are burned during the workout. The Arm Circles Calories Burned Calculator estimates the number of…
To find the date 60 days before today, simply count backward from the current date by 60 days. You can use a date calculator to simplify this calculation. 60 Days Before Today Calculator Today’s Date Date 60 Days Before Today Calculate Reset The 60 Days Before Today Calculator lets you retrospect the exact date that…

10 / 100 SEO Score Enter the values in fields of basic and advanced acceptable age gap calculator to find out the answer. Knowing the right age gap in relationships can be difficult, but the “half your age plus 7” rule provides a useful answer. This rule, often used to calculate socially acceptable age differences,…