RF Value Calculator
To calculate the Rf value in chromatography, measure the distance the solute travels from the origin and divide it by the distance the solvent front travels. This simple division provides the retention factor, or Rf, value.
To calculate the Rf value in chromatography, measure the distance the solute travels from the origin and divide it by the distance the solvent front travels. This simple division provides the retention factor, or Rf, value.
In chromatography, the Rf value (retention factor) is integral for analyzing and comparing substances. It serves to identify compounds based on their movement across a stationary phase relative to a solvent. Different compounds have unique Rf values due to factors like polarity and solubility.
For instance, pigments or amino acids will have varying Rf values that indicate their purity and identity in the mixture. Scientists and researchers use these values to examine chemical behavior and properties in fields like biochemistry, pharmaceuticals, and environmental studies.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| DSU | Distance traveled by the solute |
| DSV | Distance traveled by the solvent front |
Example 1:
Suppose the solute travels 3 cm, and the solvent front reaches 6 cm.
| Step | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Solute Distance (DSU) | 3 cm |
| Solvent Distance (DSV) | 6 cm |
| Rf Calculation | |
| Result | 0.5 |
Answer: The Rf value is 0.5.
Example 2:
If the solute covers 5 cm and the solvent front 10 cm:
| Step | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Solute Distance (DSU) | 5 cm |
| Solvent Distance (DSV) | 10 cm |
| Rf Calculation | |
| Result | 0.5 |
Answer: The Rf value is 0.5.
The RF Value Calculator is a retention factor measuring tool. It is specifically used in chromatography for finding out the retention factor or RF value. This factor measures how far a compound travels relative to the solvent front on a chromatography plate.
This value is instrumental in analyzing and identifying various substances. As a matter of fact, different compounds have unique RF values based on factors like polarity, solvent type, and interaction with the stationary phase.
To calculate the RF value, you can use the formula RF = Distance traveled by the compound / Distance traveled by the solvent front.
For example, if a compound moves 2 cm on the TLC plate and the solvent front moves 5 cm, the RF value is 0.4. This tool enables precise and efficient calculation of RF values, making it easier to analyze chromatography results.
In a word, the RF Value Calculator simplifies chromatography analysis, providing accurate RF values to assist in identifying compounds and assessing purity in mixtures.
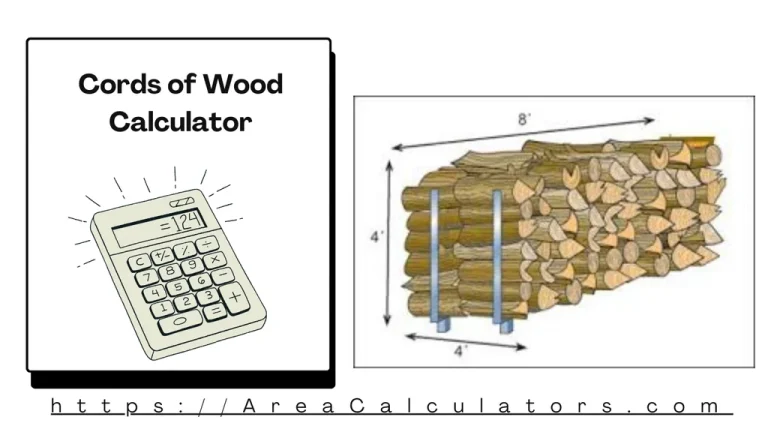
To calculate the cords of wood, multiply the length, width, and height of the woodpile in feet and divide the result by 128. A Cords of Wood Calculator is a handy tool to determine the volume of firewood in cords. A cord is a standard measurement used in forestry and firewood sales, equal to 128…
10 / 100 SEO Score To calculate the Antecedent Precipitation Index (API), multiply the previous day’s API value by a decay factor kk, then add the precipitation (P) from the current day. The Antecedent Precipitation Index (API) Calculator is used to estimate soil moisture conditions based on recent precipitation. This index is widely used in…
To convert milliequivalents per liter (mEq/LmEq/L) to milligrams per liter (mg/Lmg/L), multiply mEq/LmEq/L by the molar mass of the substance and divide by its valence. The Meq/L to Mg/L Calculator is a useful tool for converting concentrations from milliequivalents per liter to milligrams per liter. This conversion is often required in medical, chemical, and environmental…
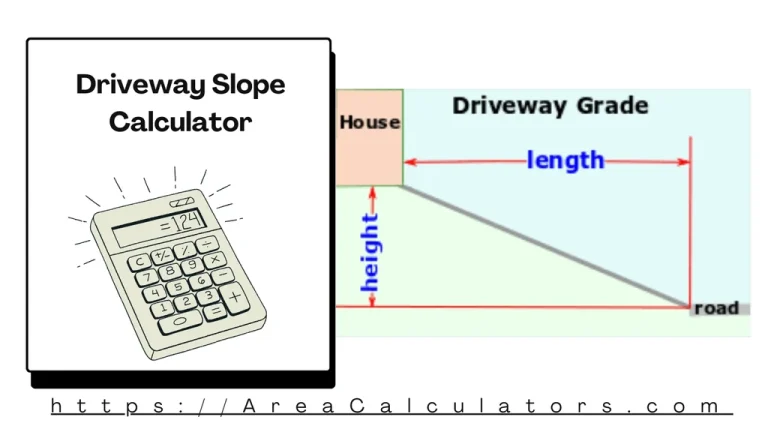
Divide the rise (vertical distance) by the run (horizontal distance), then multiply by 100 to find the slope percentage. The Driveway Slope Calculator helps determine the slope or incline of a driveway to ensure it meets safety and drainage standards. Proper slope calculation is essential for preventing water pooling and ensuring vehicles can navigate the…
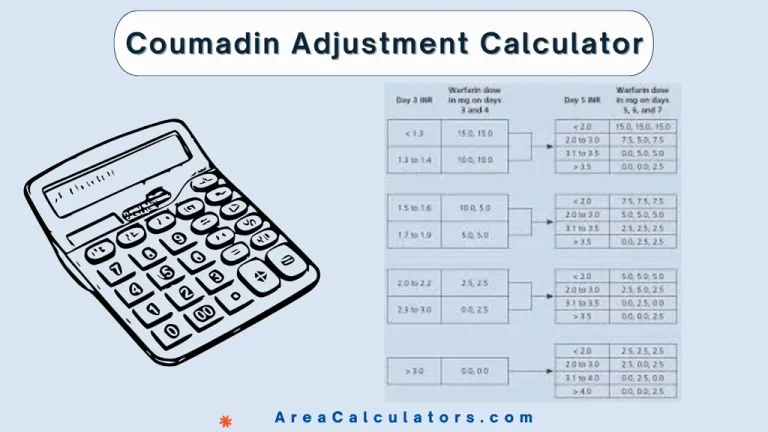
7 / 100 SEO Score To adjust Coumadin (warfarin) dosage based on INR, first identify the current INR level and the target INR. Multiply the initial dose by the ratio of the target INR to the current INR, and this will give you the adjusted dose. The Coumadin adjustment calculator is used to calculate…

10 / 100 SEO Score First, multiply your years by 365 to account for the total days in full years. Then, multiply your months by 30 to approximate the number of days for partial years. Finally, add any extra days to get the total age in days. An Age in Days Calculator converts your age…