Rev Per Mile Calculator
To calculate revolutions per mile (RevPM), divide the number of inches in a mile (63,360) by the product of the tire diameter and π (pi).
To calculate revolutions per mile (RevPM), divide the number of inches in a mile (63,360) by the product of the tire diameter and π (pi).
The Rev Per Mile Calculator is an essential tool for vehicle owners and fleet managers. It determines the number of tire revolutions required to travel a mile, which directly affects speedometer accuracy, fuel efficiency, and overall performance.
RevPM = 63,360 / (D × π)
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| RevPM | Revolutions per mile |
| D | Tire diameter (in inches) |
| π | Pi constant (~3.1416) |
Example 1: Tire Diameter 30 Inches
| Step | Value |
|---|---|
| Tire Diameter (D) | 30 inches |
| Revolutions Per Mile (RevPM) | 63,360 ÷ (30 × π) ≈ 670.2 RevPM |
Example 2: Tire Diameter 33 Inches
| Step | Value |
|---|---|
| Tire Diameter (D) | 33 inches |
| Revolutions Per Mile (RevPM) | 63,360 ÷ (33 × π) ≈ 610.7 RevPM |
The Rev Per Mile Calculator is a helpful tool designed to calculate the number of tire revolutions per mile, based on the tire size or other relevant parameters.
This calculator is commonly used in automotive settings to assess vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and odometer accuracy.
For instance, if you have a specific tire size like 11R22.5, the calculator can determine its revolutions per mile using the tire’s diameter.
It is particularly beneficial for truckers, fleet operators, and car enthusiasts who need precise tire measurements to maintain vehicle efficiency.
To end it, the Rev Per Mile Calculator ensures accurate and reliable calculations for tire revolutions, supporting better vehicle performance and fuel economy. It’s an essential tool for maintaining optimal tire functionality.
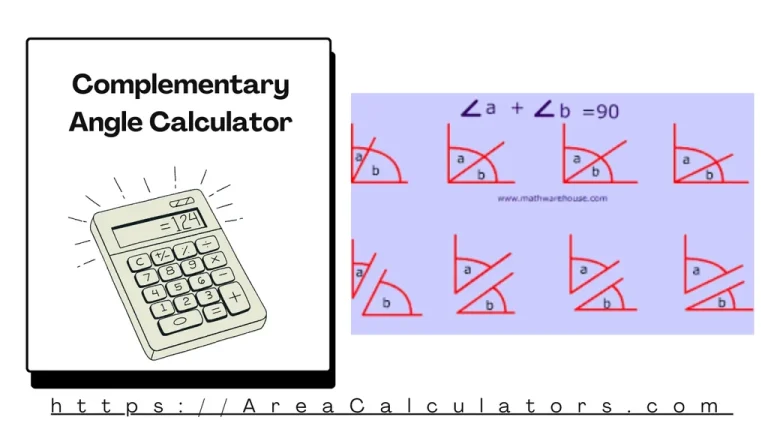
Subtract the given angle from 90° to find its complementary angle. The Complementary Angle Calculator determines the complement of a given angle in degrees or radians. Complementary angles are two angles that add up to 90°. Formula: A = 90 − a Variable Definition Units A Complementary angle Degrees (°) a Given angle Degrees (°)…
To calculate the drop rate in drops per minute (gtt/min), multiply the flow rate in mL/hr by the drop factor, then divide by 60. The Ml/Hr to Gtt/Min Calculator is a reliable and efficient tool for converting milliliters per hour (mL/hr) into drops per minute (gtt/min). It simplifies IV fluid management by ensuring accurate drip…

To calculate kW to kWh Cost, divide the total cost (TC) by the product of power in kilowatts (P) and time in hours (T). This determines the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh), helping you evaluate energy expenses efficiently. The kW to kWh Cost Calculator is a vital tool for estimating electricity expenses based on power usage…
Multiply 2 by the square of the antenna diameter (D²) and divide by the wavelength (λ) to determine the far-field distance. The Far-Field Calculator is a crucial tool for understanding the range at which electromagnetic waves from antennas can be considered parallel and undisturbed by near-field interactions. Engineers, physicists, and communication specialists often use this…
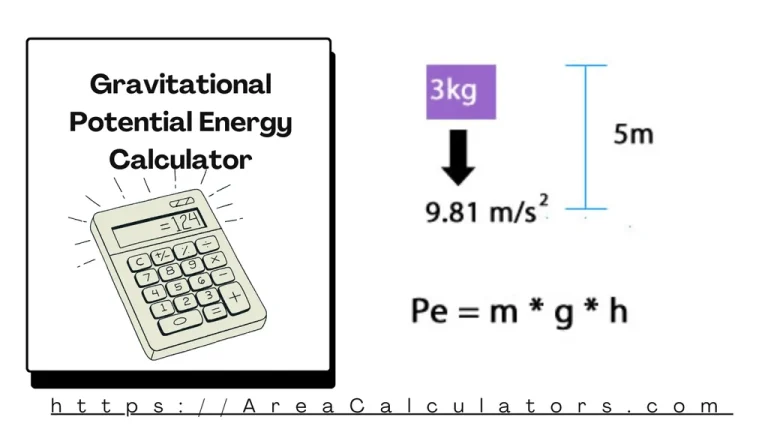
Gravitational potential energy is calculated by determining the work needed to move an object from a reference point to a position within a gravitational field. The Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator simplifies the process of calculating the energy stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field. Formula: U=−G⋅M⋅mrU = -\frac{G \cdot M…
To determine the air exchange rate, divide the airflow rate (QQ) by the room volume (VV). This calculation provides the number of air changes per hour (ACH) or minute, helping ensure proper ventilation. The Air Exchange Calculator is a crucial tool for assessing ventilation effectiveness in spaces like homes, offices, and industrial buildings. By calculating…